Software
 Computational Robotics
Computational Robotics
- OMPL
-
 OMPL is a lightweight, thread-safe, easy to use, and extensible library for sampling-based motion planning. The code is written in C++, includes Python bindings and is released under the BSD license. OMPL is also integrated with ROS. On top of the OMPL library, we have developed OMPL.app: a GUI for rigid body motion planning that allows users to load a variety of mesh formats that define a robot and its environment, define start and goal states, and play around with different planners.
OMPL is a lightweight, thread-safe, easy to use, and extensible library for sampling-based motion planning. The code is written in C++, includes Python bindings and is released under the BSD license. OMPL is also integrated with ROS. On top of the OMPL library, we have developed OMPL.app: a GUI for rigid body motion planning that allows users to load a variety of mesh formats that define a robot and its environment, define start and goal states, and play around with different planners.
- VAMP
 VAMP (Vector Accelerated Motion Planning) is a state-of-the-art motion planning library that leverages single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) parallelism to achieve order-of-magnitude speedups in motion planning.
Combined with the collision-affording point tree (CAPT), VAMP is able to achieve microsecond-scale planning times on dynamic, unmodeled environments, enabling real-time motion planning performance.
VAMP (Vector Accelerated Motion Planning) is a state-of-the-art motion planning library that leverages single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) parallelism to achieve order-of-magnitude speedups in motion planning.
Combined with the collision-affording point tree (CAPT), VAMP is able to achieve microsecond-scale planning times on dynamic, unmodeled environments, enabling real-time motion planning performance.
- Planner Arena
-
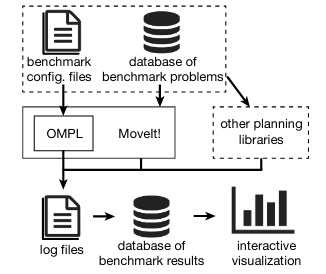 Planner Arena is a site for benchmarking sampling-based planners. The site is set up to show the performance of implementations of various sampling-based planning algorithms in the Open Motion Planning Library (OMPL).
Planner Arena is a site for benchmarking sampling-based planners. The site is set up to show the performance of implementations of various sampling-based planning algorithms in the Open Motion Planning Library (OMPL).
- Robowflex
-
 Robowflex is a library that makes using MoveIt for motion planning easy, providing a high-level C++ API that simplifies many common use-cases in motion planning research, such as benchmarking, customization, and accessing underlying datastructures.
Robowflex is a library that makes using MoveIt for motion planning easy, providing a high-level C++ API that simplifies many common use-cases in motion planning research, such as benchmarking, customization, and accessing underlying datastructures.
- MotionBenchMaker
-
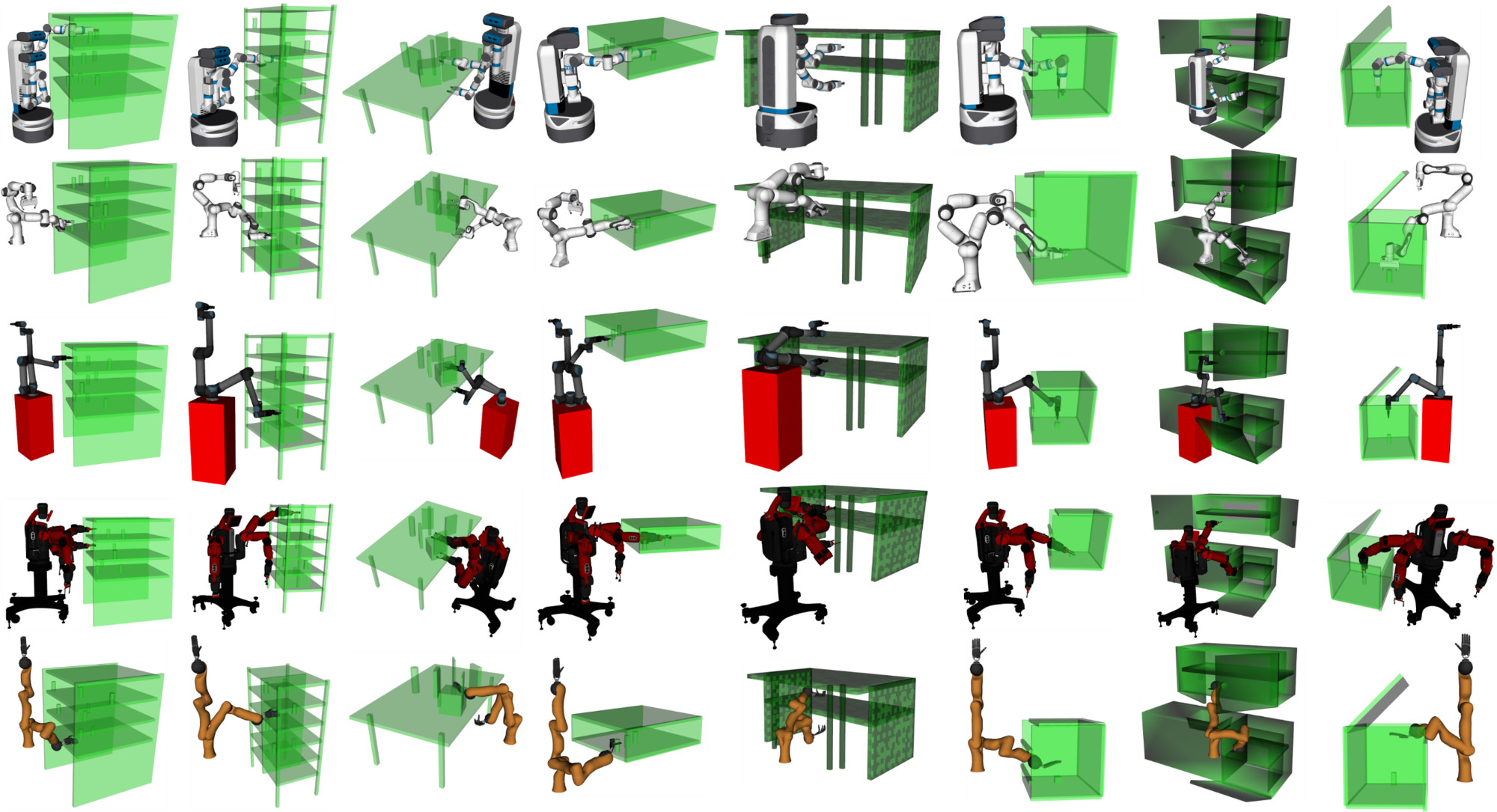 MotionBenchMaker is an extensible, easy-to-use tool to generate and benchmark datasets for manipulation problems. In addition to the tool to generate datasets, MotionBenchMaker comes with a suite of over 40 prefabricated datasets, with 5 different commonly used robots in 8 environments.
MotionBenchMaker is an extensible, easy-to-use tool to generate and benchmark datasets for manipulation problems. In addition to the tool to generate datasets, MotionBenchMaker comes with a suite of over 40 prefabricated datasets, with 5 different commonly used robots in 8 environments.
- TMKit
-
 The Task-Motion Kit (TMKit) is a framework for Task and Motion Planning. Everyday activities, e.g., setting a table or making coffee, combine discrete decisions about objects and actions with geometric decisions about collision free motion. TMKit jointly reasons about task-level objectives, i.e., choosing actions and objects, and motion-level objectives, i.e., finding collision free paths.
The Task-Motion Kit (TMKit) is a framework for Task and Motion Planning. Everyday activities, e.g., setting a table or making coffee, combine discrete decisions about objects and actions with geometric decisions about collision free motion. TMKit jointly reasons about task-level objectives, i.e., choosing actions and objects, and motion-level objectives, i.e., finding collision free paths.
- HyperPlan
- HyperPlan is a hyperparameter optimization framework for selecting, tuning, and optimizing motion planning performance. Given a dataset, the best planner and configuration for that planner can be selected to maximize arbitrary cost functions such as planning time, combined planning time and path cost, etc.
- OOPSMP
- OOPSMP is a package for motion planning that is easy to extend, robust, and efficient. It can be used for motion planning research or as a teaching tool. This package is still available for download, but is no longer further developed (except for minor bug fixes).
 Computational Biomedicine
Computational Biomedicine
- PROTEAN-CR
- This is the front end to most of the webservers that implement our work in structural computational biology (currently EnGens, DINC-Ensemble, DINC-Covid) and our work in structural immunoinformatics (APE-Gen 2.0, 3pHLa, HLA-Arena, and PepSim). Detailed explanations of the corresponding tools are provided in the following tool descriptions. See PROTEAN-CR in the wider Informatics Technology for Cancer Research (ITCR) ecosystem here.
- APE-Gen 2.0
- APE-Gen 2.0 performs Class I pMHC structural modeling, including post-translational modifications and non-canonical peptide geometries.
- EnGens
- Unsupervised learning algorithms to generate representative conformational ensembles from protein conformational datasets
- DINC-Ensemble
- DINC-Ensemble docks large ligands incrementally to an ensemble of protein receptors. In case one receptor conformation is provided, this becomes protein-ligand docking.
- HLA-Arena
- HLA-Arena provides a customizable environment for the structural modeling and analysis of peptide-HLA complexes.
- 3pHLA
- Given a pMHC structure, 3pHLA can acurately predict binding affinities and prioritize good peptide binders.
- PepSim
- PepSim is a novel score that predicts T-cell cross-reactivity based on the structural and biochemical similarity of human pMHCs.
- DINC-Covid
- DINC-Covid docks ligands to ensembles of Sars-Cov2 protein receptors.
- SARS-Arena
-
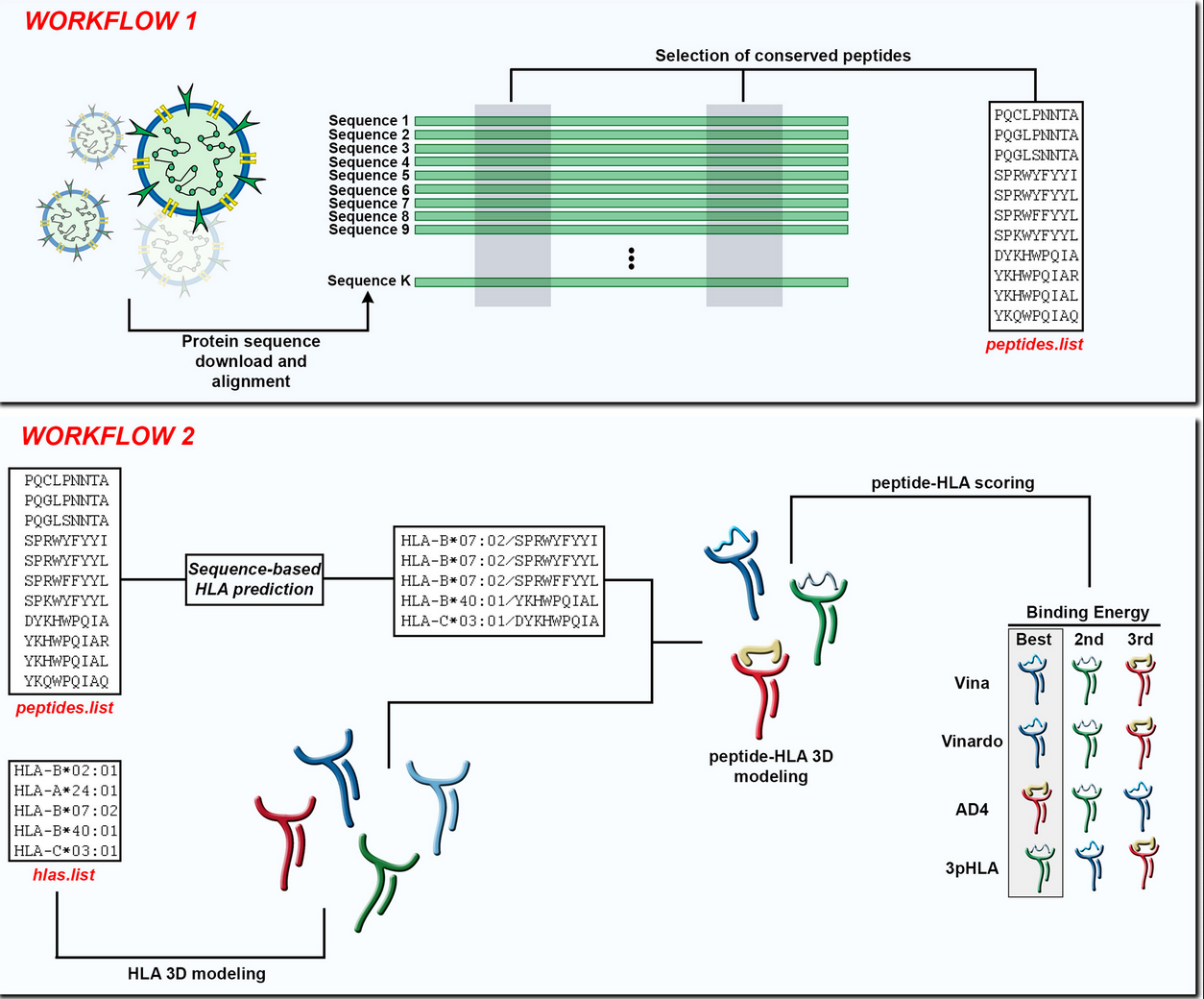 A Pipeline for Selection and Structural HLA Modeling of Conserved Peptides from SARS-related Coronaviruses for Novel Vaccine Development.
A Pipeline for Selection and Structural HLA Modeling of Conserved Peptides from SARS-related Coronaviruses for Novel Vaccine Development.
- Metabolite Translator
-
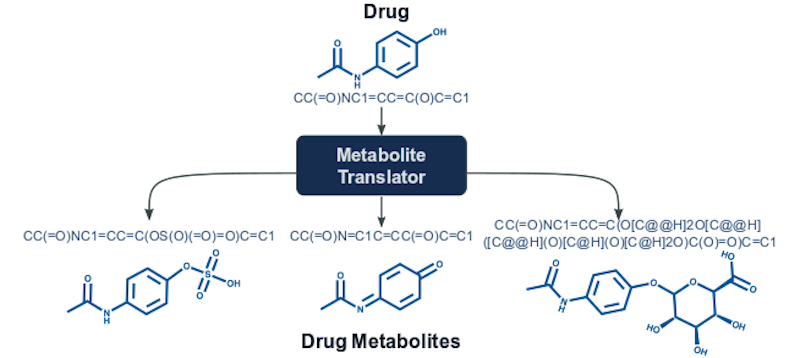 Metabolite Translator predicts human metabolites for small molecules including drugs. It is build upon a Neural Machine Translation algorithm representing molecules as sequences using the SMILES notation. Metabolite Translator converts the SMILES of the initial molecule into the SMILES representations of the metabolites that can be possibly formed in the human body. The method has been trained on data that cover metabolism of xenobiotics as well as endogenous compounds and therefore it can predict metabolites through a wide range of enzymes including the enzymes of phase I and phase II drug metabolism.
Metabolite Translator predicts human metabolites for small molecules including drugs. It is build upon a Neural Machine Translation algorithm representing molecules as sequences using the SMILES notation. Metabolite Translator converts the SMILES of the initial molecule into the SMILES representations of the metabolites that can be possibly formed in the human body. The method has been trained on data that cover metabolism of xenobiotics as well as endogenous compounds and therefore it can predict metabolites through a wide range of enzymes including the enzymes of phase I and phase II drug metabolism.
- pHLA-RF
-
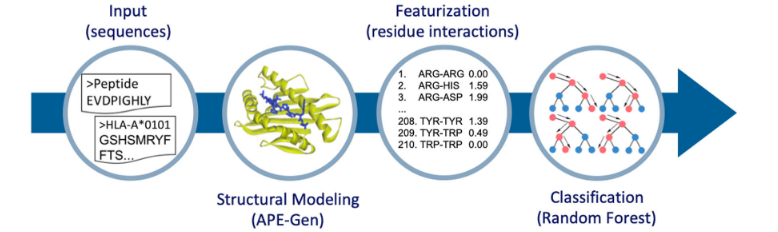 Large-Scale Structure-Based Prediction of Stable Peptide Binding to Class I HLAs Using Random Forests.
Large-Scale Structure-Based Prediction of Stable Peptide Binding to Class I HLAs Using Random Forests.
- LabelHash
-
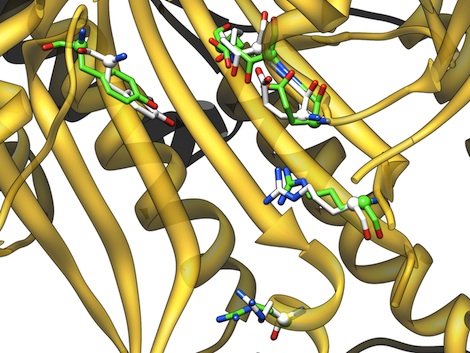 A web server for matching 3D structural motifs in proteins against the proteins in the Protein Data Bank. With a plugin for Chimera the match results can be visualized.
A web server for matching 3D structural motifs in proteins against the proteins in the Protein Data Bank. With a plugin for Chimera the match results can be visualized.
- FASST
- FASST Live is a web server for identifying clusters of proteins that share local structural similarity. (Private use)
- RACOGS
- A web server for reconstructing all-atom protein structures from coarse grain structures. (Private use)